Research News
Effects of paraformic acid supplementation, as an antibiotic replacement, on growth performance, intestinal morphology and gut microbiota of nursery pigs
Yuyi Zhong, Bin Zuo, Jiaqi Li, Yafeng Zhai*, Richard Mudarra* Abstract A total of 150 crossbred male pigs (21 ± 1 days old; 8.85 ± 0.15 kg body weight [BW]) were randomly assigned to five dietary treatments with five replicates per treatment and six pigs per pen to evaluate the effect of paraformic acid (PFA), as a substitute to antibiotics, on growth performance, intestinal morphology, and gut microbiota of nursery pigs. The treatments were: 1) Negative control (NC): nutrient adequate control diet; 2) PFA1: similar to NC plus 0.30% PFA; 3) PFA2: similar to NC plus 0.60% PFA; 4)...
Enhanced Control of Salmonella and Escherichia coli by Paraformic Acid Compared to Conventional Formic Acid and Formaldehyde: MIC and Feed Contamination Studies
MAREK LEJA1; KASEN ZHAI2 1 ETOS Czesław Szymendera Sp. z o.o, Poland; 2 Numega Nutrtion Pte.Ltd, Singapore BACKGROUND Ensuring the microbiological safety of animal feed is critical not only for livestock health but also for the safety of meat, milk, and eggs entering the human food chain [1]. Feed ingredients may harbor chemical contaminants (e.g., mycotoxins) as well as bacterial pathogens capable of colonizing food-producing animals—cattle, poultry, swine, and turkeys—which serve as reservoirs for organisms such as Campylobacter spp., non-Typhi Salmonella enterica, Shiga toxin–producing Escherichia coli, and Listeria monocytogenes [2]. Among these, Salmonella remains a leading cause of...
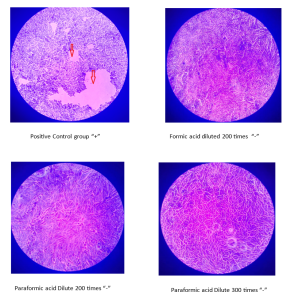
Paraformic Acid Can Effectively Inhibit Avian Influenza Viruses (H9N2) At A Concentration Of 2.3 ml/L
Recently, Numega cooperated with a licensed third-party laboratory to conduct virus research on the inhibitory effect of paraformic acid on the avian influenza virus H9N2. Chicken embryo cells were infected with 1.0×106CFU/mL concentrations of virus, and the infected chicken embryo cells were incubated with different concentrations of paraformic acid and formic acid at 37 degrees for 10 minutes. The cells were stained and the cell surface morphology was observed under a microscope. The results showed that the log10 values of formic acid diluted 200 times (4.25 mL/L) and paraformic acid diluted 300 times (2.3 mL/L) were the same, both...
Paraformic Acid as an Effective Additive in the Control of Pathogenic Bacteria in Fish and Shrimp
By Richard Mudarra (Colleague of Agriculture, University of Panama, Panama). The global aquaculture market was valued at $204 billion in 2020 and is expected to reach $262 billion by the end of 2026. Besides the unstoppable growth of the fish industry, the seafood and fishing sector is facing many challenges, such as climate change and high mortalities of fish due to bacterial diseases. Among the various bacterial agents associated with fish disease in tropical environments, Streptococcus agalactiae and Edwardsiella ictaluri are responsible of high mortality in tilapia and catfish production systems, respectively, which can reach between 80% and 100% mortality in outbreaks. Furthermore, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, a...
- 1
- 2






 English
English German
German Arabic
Arabic Thai
Thai Vietnamese
Vietnamese Spanish
Spanish French
French Chinese
Chinese Japanese
Japanese